What you need to know about magnesium
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, from nerve and muscle function to protein synthesis and blood sugar regulation. Not only is magnesium essential to optimal health, but it has also been researched for its ability to prevent chronic inflammatory diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, hypertension, and heart disease.
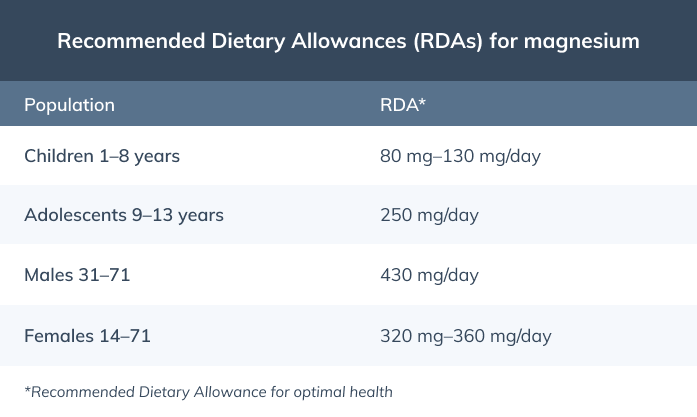
How much magnesium do you need?
Many people don’t consume enough magnesium each day; in fact, 48% of Americans and 34% of Canadians consume inadequate amounts of magnesium in their diets. The Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) for magnesium are outlined in the table below.
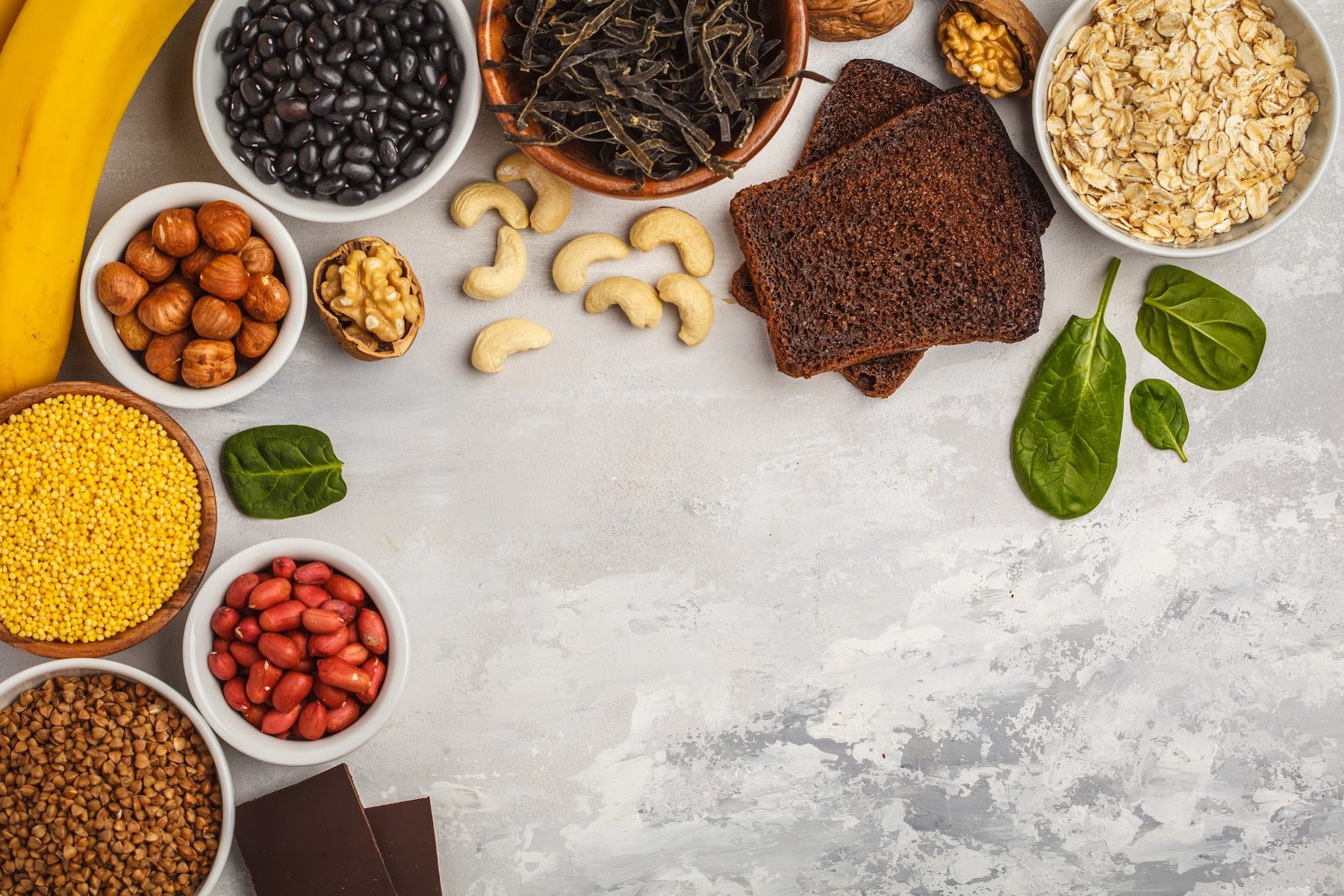
Dietary sources of magnesium
Magnesium is largely found in plant-based foods, such as pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate, bananas, and avocados, and is also available in supplement form. Include a variety of magnesium-rich foods in your diet to help you meet the RDA for magnesium.
Top benefits of magnesium
1. Boosts mood
Magnesium is closely associated with improved mental health outcomes due to its role in supporting brain biochemistry and neurotransmitter regulation. Research shows that low levels of magnesium can increase the risk of depressive behavior in adults, specifically in those under the age of 65.
2. Protects against inflammation
Magnesium acts as an antioxidant by protecting the mitochondria from the oxidative stress that can contribute to the development of these inflammatory conditions. Oxidative stress and inflammation associated with age-related conditions are correlated with low intake of magnesium-rich foods, and many chronic inflammatory conditions such as hypertension, breast and colon cancer, obesity, and heart disease have been associated with magnesium insufficiency.
3. Reduces insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition that occurs when both muscle and liver cells lose their ability to effectively absorb glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream. Insulin resistance plays a significant role in the development of chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Low levels of magnesium have been associated with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, and research suggests that high dietary magnesium intake may be protective against insulin resistance.
4. Helps to manage blood pressure
Magnesium also plays a role in managing blood pressure in patients with high blood pressure (hypertension). Research suggests that oral magnesium supplementation reduces blood pressure in patients with mild hypertension. Low levels of dietary magnesium may also negatively affect blood pressure regulation, highlighting the vital role magnesium plays in maintaining optimal blood pressure.
5. Improves athletic performance
Magnesium is necessary for many essential functions during exercise, such as maintaining electrolyte balance, blood oxygenation, and energy production. Magnesium is also lost through perspiration (sweating) that occurs during strenuous exercise, making it even more important to replenish magnesium stores. Research demonstrates that increasing magnesium consumption through diet or supplementation can increase athletic performance if you’re deficient.